
A multilayer printed circuit board (PCB) is a type of circuit board that consists of more than two layers of conductive material separated by insulating layers. These boards are used in electronic devices where the complexity of the circuit requires more routing channels than can be provided by a single-layer or double-layer PCB.
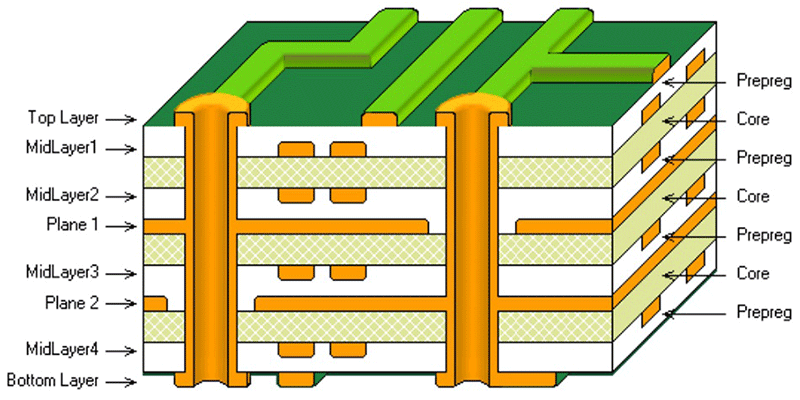
Here's a breakdown of the key differences between a multilayer PCB and a single-layer PCB:
1. Layer Structure:
Multilayer PCB: Consists of three or more conductive layers separated by insulating layers (dielectric). The conductive layers are interconnected by vias (plated holes).
Single-layer PCB: Contains only one layer of conductive material (usually copper) on one side of the insulating substrate.
2. Routing Complexity:
Multilayer PCB: Allows for complex and dense circuit designs with a high level of routing flexibility. Signal traces can be routed through multiple layers, reducing the need for long, space-consuming traces on the surface.
Single-layer PCB: Suitable for simpler circuits with less routing complexity. Components and traces are typically placed on one side of the board.
3. Space Utilization:
Multilayer PCB: Maximizes space utilization, as components and traces can be distributed across multiple layers. This is crucial for miniaturization and compact designs.
Single-layer PCB: Requires more space for routing, limiting the design options in terms of size and layout.
4. Signal Integrity:
Multilayer PCB: Offers improved signal integrity due to the ability to separate and shield different signal layers, reducing interference and crosstalk.
Single-layer PCB: More susceptible to signal interference since all traces are on the same layer.
5. Applications:
Multilayer PCB: Commonly used in complex electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, networking equipment, and advanced control systems.
Single-layer PCB: Found in simpler electronic devices and applications where cost, size, and complexity are less critical.
6. Manufacturing Complexity:
Multilayer PCB: Involves a more complex manufacturing process, including layer alignment, lamination, and drilling for vias.
Single-layer PCB: Simpler and more cost-effective to manufacture.
In summary, while single-layer PCBs are suitable for simpler designs, multilayer PCBs offer a higher degree of complexity, flexibility, and performance, making them essential for advanced electronic devices with intricate circuitry and miniaturized designs.
Get more knowledge about difference between multilayer PCB and single-layer PCB please refer to Rigaopcb:https://www.rigaopcb.com/