The production of printed circuit boards (PCBs) necessitates a vital phase referred to as Circuit Card Assembly (CCA). This process is complicated yet Essential in the electronics sector. This manual offers an understanding of the fundamental features of Circuit Card Assemblies. This includes different types, main parts, and complete steps involved in making electronic devices function.
Making a Circuit Card Assembly (CCA) is like creating fine art. It's a key step in making printed circuit boards (PCBs). You start with a thin layer that doesn't allow electricity to pass through. Gradually, we add electrical paths to it until it turns into a fully functioning circuit board.
Specialists use methods like Surface Mount Technology and Through-Hole Technology, and automatic machines, to create these circuit boards. The use of these boards is very diverse - they help operate everyday household items like smartphones and microwaves. They are also essential to complex systems used in the aerospace industry and the military.
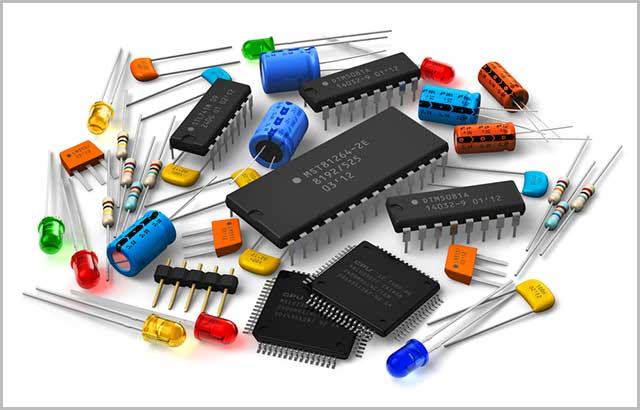

A Circuit Card Assembly, often called a Printed Circuit Board Assembly or PCB Assembly, basically has four parts.
This PCB Assembly is the core of any electronic device, acting as the base for all the other parts of the device. It's crucial for how well the device works.
An interesting thing about the PCB Assembly is that it's not just one thing. They're separate parts that make up the total assembly. These parts are really important and there are four of them.
No matter the final look and use of the gadget, every circuit board assembly basically has these four main parts.
Whether you're making, working with, or just viewing a Circuit Card Assembly, it's important to know these four main components. They're the building blocks of all Circuit Card Assemblies. Despite the many complexities and differences in various electronics, these four parts are always there.
1. Substrate: The foundational layer that binds electronic components together. It is available in flexible, rigid, and metalcore forms, each designed to suit various electronic devices.
2. Copper: A layer of copper foil that, when laminated onto the substrate, forms conductive tracks or traces.
3. Solder Mask: A protective coating that imparts the characteristic tint to circuit boards. It prevents corrosion and ensures proper component placement during the reflow oven process.
4. Silkscreen: The highest layer shows icons and words to help engineers know how the board works.
We're here to talk about and make sense of various ways to put things together. We strive to comprehend the usage of these diverse methods, their functionality, and what sets them apart.
We'll discuss their main traits and why they function as they do. The idea is to really get these assembly methods, by diving into what sets each one apart.
Let's journey through these assembly techniques and learn about them in a simple and enlightening manner.
1. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Assembly:
This technique is suitable for compact and automated production, providing high-density circuits. Although not suitable for every component, it is an efficient method for many electronic devices.
2. Box Build Assembly:
This involves system integration, ranging from basic enclosures to intricate Technical systems.
3. Through-Hole Technology:
This method involves inserting wires into holes on the circuit board and soldering them on the other side. Despite being less common with the advent of SMT, it is still suitable for specific applications like Electric capacitors.
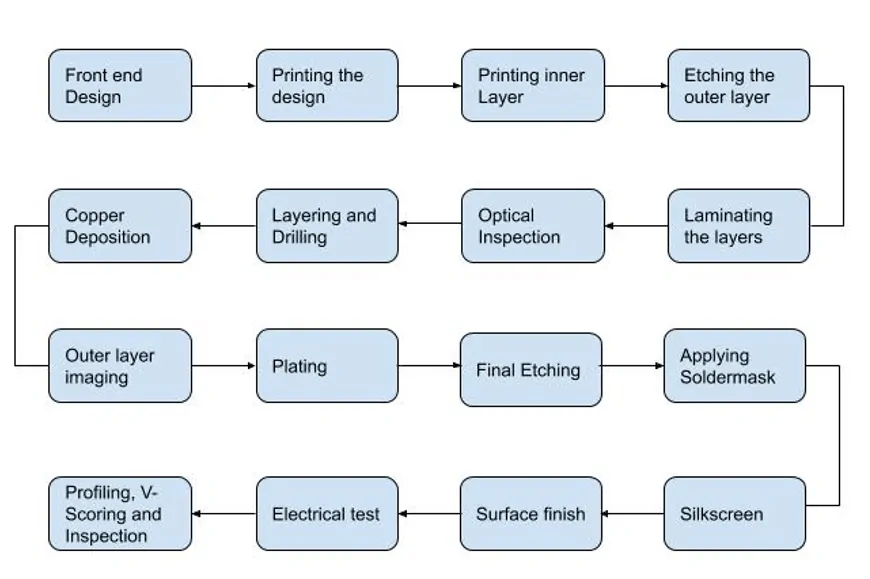
Building a Circuit Card Assembly is like creating a beautiful piece of music. It involves many steps that work together, like the different parts of a symphony. Each step, like each part of a symphony, adds something important to the final product. This is how we make a Circuit Card Assembly.
Every step matters just as much and relies on the other steps working well for the whole process to succeed. Think of each step as a musical instrument in an orchestra. Only when they all work together, they can produce beautiful music. In this situation, they form a final, working Circuit Card Assembly.
Therefore, understanding the compilation of a Circuit Card Assembly process is just like appreciating a symphony. The process is not just a single task done alone. It's a wonderful mix of many stages working together perfectly. Like a well-played song, it carefully arranges parts to successfully build a complex circuit card.
This comparison shows how careful and precise you need to be when assembling a Circuit Card, illustrating the true effort required.
1. Applying Solder Paste Using Stencil:
This stage involves applying a solder paste to the PCB board using a template and preparing it to attach parts.
2. Automated Placement of Components:
Robots quickly and correctly put different parts on the panel.
3. Reflow Soldering:
A special oven warms up the circuit board to melt the metal and create strong links.
4. Inspection and Quality Control:
This important part includes using a computer to check the item or doing X-ray checks to make sure the finished product is perfect.
5. Through-Hole Component Insertion:
This step involves adding components that require through-hole technology.
6. Final Inspection and Functional Test:
We thoroughly check and test the put-together board to make sure it's working as it should.
When thinking about making printed circuit boards (PCBs), some key electronic parts are very important. You need them to make PCBs properly. They're like the main structure that lets PCBs work and helps the electronics they're in to run smoothly. Here, I want to talk about these important electronic parts that are really involved in making PCBs.
These parts are like the heart of a printed circuit board. Based on their composition and role in the entire design, each of them performs different tasks.
Without these parts, a printed circuit board would just be a flat, non-electric material. It wouldn't be able to make, control or help with electric signals.
In simple terms, we are discussing the essential electronic components required to construct a circuit board. These components constitute the entire PCB, enabling us to build and operate it as we typically expect from our everyday electronics. Without these, PCB making would pretty much stop, and all our modern, high-tech devices we depend on would freeze.
1. Diode: This component controls the flow of current in a single direction.
2. Capacitors: They are responsible for storing and releasing electrical energy.
3. Inductors: These components store energy in a magnetic field.
4. Transistors: They serve dual roles as switches and amplifiers.
5. Resistors: Fundamental components in all types of electronic circuits, they resist or limit the flow of current.
Picking Circuit Card Assembly provides numerous benefits. These include improved design flexibility and fast production. It is ideal in the rapidly evolving world of electronics manufacturing.
Separately, the intricate steps involved in Circuit Card Assembly have impacts beyond electronic devices. These techniques also significantly influence sectors such as aerospace and the military.