The circuit card assembly manufacturing process involves several key stages, each crucial for the successful creation of electronic circuit boards. Here are the primary stages:
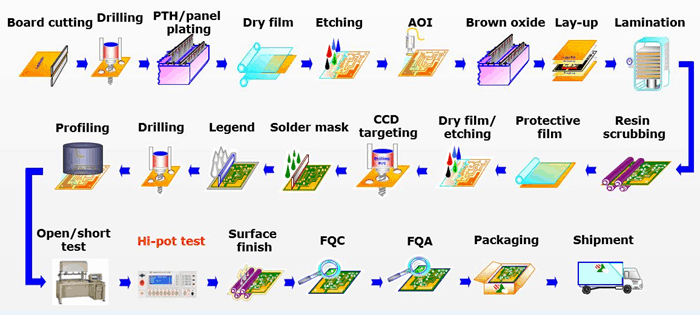
1. Design and Prototyping:
Initial conceptualization and schematic design of the circuit board.
Creation of a prototype board to test functionality and identify potential issues.
2. Materials Procurement:
Sourcing and procurement of electronic components, raw materials, and circuit board substrates.
3. Stencil Printing:
Applying solder paste to designated areas on the circuit board using a stencil. This prepares the surface for component placement.
4. Component Placement:
Automated or manual placement of electronic components onto the solder paste areas based on the circuit board design.
5. Reflow Soldering:
The circuit board is passed through a reflow oven, where heat causes the solder paste to melt and form a secure bond between components and the board.
6. Inspection and Quality Control:
Visual inspection and automated checks to identify any defects, misalignments, or soldering issues. This stage ensures the quality and reliability of the assembled board.
7. Through-Hole Assembly (if applicable):
For boards with both surface-mount and through-hole components, additional steps are taken to solder through-hole components.
8. Cleaning:
Removal of any residues, flux, or contaminants left over from the soldering process. This is essential for maintaining the long-term reliability of the circuit board.
9. Testing:
Comprehensive testing of the assembled circuit board to ensure functionality, performance, and compliance with design specifications.
10. Programming and Configuration (if applicable):
Loading software or firmware onto the board, configuring settings, and ensuring that the board functions according to its intended purpose.
11. Final Inspection:
A final round of inspection to verify that the assembled circuit boards meet quality standards and specifications.
12. Packaging and Shipping:
Packaging of the completed circuit boards for protection during transportation and delivery to customers or further stages in the supply chain.
These stages collectively ensure the successful and efficient production of circuit cards that meet the desired specifications and quality standards. The use of automated machinery, precision engineering, and rigorous quality control measures contributes to the reliability of the final products.