In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics, flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) have emerged as a game-changer, offering designers unparalleled freedom to innovate and push the boundaries of what’s possible. These bendable wonders, in contrast to their traditional rigid counterparts, have become indispensable in the fabrication of sleek, compact, and high-performance electronics devices. This article shines a light on the world of flexible PCB manufacturers, exploring how they craft these versatile components and why they are increasingly preferred over rigid boards in various applications.
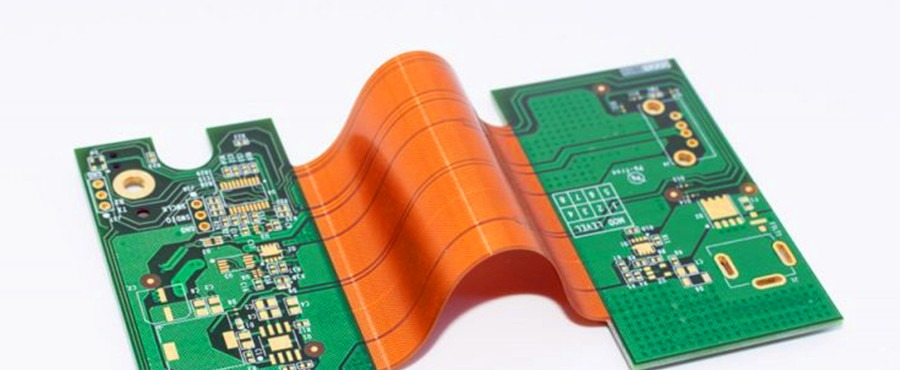
Flexible PCBs, also known as flex circuits, are made from flexible base materials, allowing them to conform to three-dimensional spaces and endure repeated bending without losing functionality. Unlike rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) that maintain a fixed shape, FPCBs open up a world of design possibilities, enabling manufacturers to create thinner, lighter, and more adaptable electronics devices.
Within the flexible PCB realm, there exists a hybrid category known as rigid-flex PCBs. These boards combine the best of both worlds: the durability and mounting stability of rigid boards with the flexibility of flex circuits. Rigid-flex PCBs are ideal for applications where a mix of rigidity for connectors and flexibility for tight spaces is required, such as in wearable technology or complex aerospace systems.
The secret behind the magic of flexible PCBs lies in the unique flex materials used in their construction. Commonly, polyimide is the go-to substrate due to its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and ability to maintain electrical properties under stress. Compared to FR4, a standard material for rigid PCBs, flex materials offer greater flexibility without compromising on performance, making them suitable for dynamic environments.
Flex PCB manufacturers employ a range of sophisticated techniques to produce these intricate components. The process begins with the design phase, often utilizing advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software to map out the circuitry. This is followed by the selection of appropriate materials, including copper layers, base films, and coverlays for protection.
Production then moves to the photolithographic process, where a photosensitive film is applied to the base material. UV light is used to expose the desired circuit pattern, which is later developed to create the conductive pathways. For double-sided or multi-layer flex circuits, additional steps are taken to align and bond the layers together.
Flex PCB manufacturers cater to a wide range of production needs, from prototyping to mass production. This versatility allows both startups and established companies to leverage the benefits of flexible circuits in their products. Custom solutions can be tailored to specific design requirements, whether it’s a single-layer flex for simple wiring or a complex rigid-flex PCB for high-end applications.
1. Space Savings: FPCBs can be bent, folded, or twisted to fit into tight spaces, significantly reducing the overall footprint of electronic devices.
2. Weight Reduction: Lightweight flex materials make FPCBs ideal for portable devices, contributing to enhanced portability and user comfort.
3. Durability: Despite their delicate appearance, flexible PCBs are resilient against vibrations and shocks, enhancing product lifespan.
4. Design Flexibility: The ability to contour around irregular shapes allows for more creative and ergonomic designs.
5. Improved Reliability: With fewer interconnections needed compared to rigid board assemblies, flexible circuits reduce the risk of failure points.
As technology pushes for ever-smarter and more integrated devices, flexible PCBs are poised to play an even more central role. From wearables and IoT devices to advanced medical equipment and autonomous vehicles, the demand for flexible circuits is only set to increase. Manufacturers who invest in the development of advanced flex and rigid-flex PCBs are not just meeting the present needs of the market; they are actively shaping the future of electronics.
In conclusion, flexible printed circuit board manufacturers are at the forefront of a technological revolution, enabling designers to break free from the constraints of traditional rigid boards. With their unique blend of adaptability, performance, and reliability, flexible PCBs are transforming how we interact with and conceive of electronics devices. As the industry continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of these flexible marvels, unlocking new horizons for innovation and pushing the boundaries of what’s technologically feasible.
1. What exactly are flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), and how do they differ from traditional rigid PCBs?
Flexible PCBs, or FPCBs, are circuit boards made with flexible base materials, such as polyimide, that allow them to bend and flex without damaging the electrical connections. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, which are made of inflexible materials like FR4 and maintain a fixed shape, FPCBs can conform to complex shapes and tight spaces, making them ideal for compact and dynamic electronic devices.
2. Why are polyimide materials commonly used in flexible PCBs?
Polyimide is a popular choice for flexible PCBs due to its exceptional properties: high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and the ability to maintain electrical conductivity even when subjected to repetitive bending or twisting. It's also lightweight and thin, which contributes to the overall flexibility and reduced weight of electronic devices.
3. Can flexible PCBs be used in high-frequency applications?
Yes, flexible PCBs can indeed support high-frequency signals. The low dielectric constant and loss tangent of materials like polyimide make them suitable for high-speed and radio frequency (RF) applications. However, careful design and shielding considerations are essential to minimize signal loss and interference.
4. How do rigid-flex PCBs differ from purely flexible PCBs?
Rigid-flex PCBs combine both rigid and flexible substrates within a single circuit board. They offer sections of rigid boards for stability and mounting of heavy components, interconnected with flexible sections that allow for bending and folding. This hybrid design is ideal for applications that require a mix of rigidity and flexibility, enhancing functionality in complex devices.
5. Are flexible PCBs more expensive to manufacture than rigid PCBs?
Generally, flexible PCBs can be more costly to produce due to the specialized materials, advanced manufacturing processes, and higher precision required. However, this cost can be offset by savings in assembly, reduced size and weight, and improved reliability, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications in the long run.
6. Can flexible PCBs be repaired or modified once they are manufactured?
Repairing or modifying flexible PCBs can be challenging due to their delicate nature and integrated design. However, minor repairs might be possible with specialized equipment and skilled technicians. It's crucial to ensure proper design and thorough testing upfront to minimize the need for post-production modifications.
7. How do flexible PCBs contribute to the miniaturization of electronic devices?
Flexible PCBs enable the creation of thinner and more compact electronic devices by allowing circuitry to be bent and folded into tight spaces, reducing the overall volume occupied. This capability is especially valuable in devices where space is at a premium, such as smartphones, wearables, and medical implants.
8. Are there any environmental concerns related to the disposal of flexible PCBs?
Like all electronic waste, flexible PCBs should be handled responsibly due to the presence of potentially harmful materials like metals and plastics. Many manufacturers follow recycling and disposal guidelines to minimize environmental impact. It's important to dispose of flexible PCBs through designated e-waste collection programs to ensure proper handling and recycling.