When it comes to developing electronic circuits, breadboards and PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) play critical roles. Each serves a unique purpose in the journey from concept to final product. In this article, we will focus on the "breadboard PCB" — a hybrid approach that combines the flexibility of breadboards with the durability and reliability of PCBs. We will explore the advantages, applications, and key features of breadboard PCBs, along with some practical tips for their use.
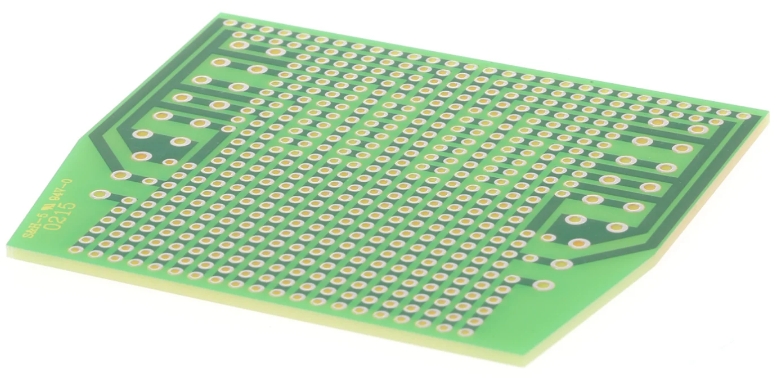
A breadboard PCB, also known as a proto board, is a type of circuit board designed specifically for prototyping. It allows engineers and hobbyists to quickly and easily build and test electronic circuits before moving on to a more permanent PCB design. Unlike traditional breadboards, which use a grid of interconnected holes, breadboard PCBs provide a more robust and reliable platform for prototyping.
Breadboard PCBs typically feature a grid layout similar to traditional breadboards. This layout makes it easy to transfer a circuit from a breadboard to a breadboard PCB without significant changes.
One of the most useful features of breadboard PCBs is the inclusion of mounting holes. These holes allow the proto board to be securely attached to a chassis or enclosure, providing stability and durability during testing and use.
Breadboard PCBs come with pre-drilled holes and copper pads or traces that facilitate soldering components in place. This ensures a more secure and reliable connection compared to the friction-fit connections used in traditional breadboards.
Many breadboard PCBs include printed component markings, such as labels for resistors, capacitors, and ICs (Integrated Circuits). These markings help users quickly identify and place components correctly, reducing the risk of errors.
Similar to traditional breadboards, breadboard PCBs often include power rails along the edges. These rails provide convenient access to power and ground connections, simplifying the process of powering the circuit.
Traditional breadboards are great for quick prototyping, but their connections can be unreliable over time. Breadboard PCBs offer a more durable solution, with soldered connections that are less prone to failure.
Soldered connections on a breadboard PCB provide better electrical conductivity and stability, reducing the risk of intermittent connections and signal issues.
Breadboard PCBs make it easy to transition from a breadboard prototype to a more permanent PCB design. The grid layout and component markings help ensure that the final design closely matches the prototype.
Using a breadboard PCB can give your prototype a more professional appearance, which can be important when presenting your design to clients, investors, or team members.
Breadboard PCBs are ideal for prototyping and development. They allow engineers and hobbyists to build and test circuits quickly, making it easy to iterate on designs and troubleshoot issues.
In educational settings, breadboard PCBs provide a hands-on way for students to learn about electronics and circuit design. The durability and reliability of breadboard PCBs make them a great choice for classroom use.
For hobbyists working on DIY electronics projects, breadboard PCBs offer a convenient and reliable way to build and test circuits. The ability to securely mount the proto board and solder components in place makes these PCBs a popular choice for home projects.
In some cases, breadboard PCBs can be used for small batch production. Their ease of use and reliability make them suitable for producing a limited number of units for testing or small-scale distribution.
Before you start soldering components to your breadboard PCB, take some time to plan your layout. Consider the placement of power rails, components, and connections to ensure a clean and organized design.
Take advantage of the mounting holes to securely attach your breadboard PCB to a chassis or enclosure. This will provide stability and protect your circuit from physical damage.
If your breadboard PCB doesn't include component markings, consider labeling your components with a marker or label maker. This will help you keep track of your design and make troubleshooting easier.
Before applying power to your circuit, double-check all connections to ensure they are correct. This will help prevent short circuits and other issues that could damage your components.
A multimeter can be a valuable tool when working with breadboard PCBs. Use it to check for continuity, measure voltages, and troubleshoot issues with your circuit.
A breadboard is a reusable platform for building and testing circuits without soldering. A breadboard PCB, or proto board, is a more permanent solution that allows for soldered connections, providing enhanced durability and reliability.
While breadboard PCBs are primarily designed for prototyping, they can be used for small batch production. However, for larger scale production, it's recommended to design a custom PCB that meets the specific requirements of your project.
Components are secured on a breadboard PCB by soldering them to the copper pads or traces. This provides a stable and reliable connection compared to the friction-fit connections used in traditional breadboards.
Breadboard PCBs offer enhanced durability, improved reliability, ease of transition from prototype to production, and a more professional appearance compared to traditional breadboards.
While it's possible to desolder components and reuse a breadboard PCB, this can be time-consuming and may damage the board. It's generally more practical to use a new breadboard PCB for each project.
Breadboard PCBs can be used for high-frequency circuits, but it's important to consider factors such as trace layout and component placement to minimize signal interference and loss.
Breadboard PCBs bridge the gap between traditional breadboards and custom PCBs, offering a durable and reliable solution for prototyping and small batch production. With their grid layout, mounting holes, and copper pads, breadboard PCBs provide a robust platform for building and testing electronic circuits. Whether you're an engineer, hobbyist, or educator, incorporating breadboard PCBs into your projects can enhance your prototyping process and lead to more successful designs.