In the realm of modern electronics manufacturing, the assembly of circuit cards stands as a cornerstone of innovation and functionality. The process of creating these vital components, which are the lifeblood of electronic devices, is both an art and a science. This article aims to shed light on the experience of circuit card assembly (CCA) and how it fits into the larger picture of electronics manufacturing.
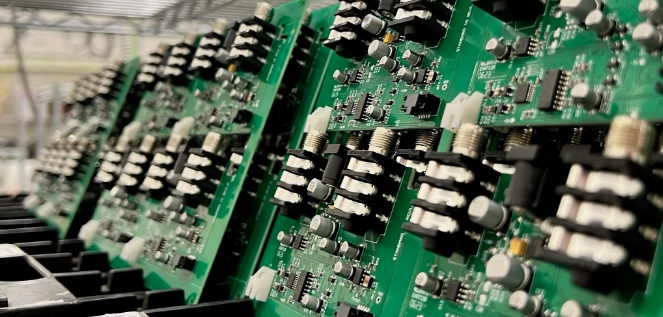
At the heart of every electronic device lies a printed circuit board (PCB). This board serves as the foundation where various electronic components are mounted. The assembly of these boards, known as printed circuit board assembly (PCBA), is a meticulous process that requires precision and attention to detail.
Integrated circuits (ICs) are a crucial element in PCBs. These tiny electronic components are responsible for the functionality of the PCB, housing thousands of transistors, resistors, and capacitors in a compact space. They are the brains of the operation, dictating the capabilities and performance of the final electronic device.
With the advent of high-frequency technologies, the demand for high-performance PCBs has skyrocketed. In sectors like telecommunications and advanced computing, the ability of a PCB to handle high-frequency signals is critical. This has pushed electronics manufacturing to new heights, requiring the assembly process to adapt and innovate continuously.
Quality control is paramount in electronics manufacturing. A high-quality PCB assembly is one that not only looks flawless but performs impeccably over time. To achieve this, manufacturers implement rigorous testing protocols at various stages of the assembly process, ensuring that each PCB meets the industry standards for reliability and performance.
Wave soldering is a time-tested method used in PCB assembly. It involves passing the PCB over a wave of molten solder that attaches electronic components directly onto the surface. This technique is favored for its efficiency and effectiveness in creating strong, durable bonds between components and the board.
Surface mount technology (SMT) assembly represents the evolution of PCB assembly techniques. SMT allows for the placement of smaller components onto the PCB, which is essential for modern electronics that require compact, high-density designs. The process involves applying solder paste to the board, placing components with high precision, and then moving the board through a reflow soldering oven to create the solder joints.
Reflow soldering is integral to SMT assembly. After component placement, the PCB is subjected to controlled heat in a reflow oven. The temperature is carefully ramped up to melt the solder paste, allowing it to flow and create solid connections between the components and the board. Once cooled, the solder solidifies, completing the assembly.
A solder mask is an essential layer on the PCB that prevents short circuits by protecting the copper traces from accidental contact with solder or conductive bits. This green or sometimes other colored layer defines where solder should be applied and helps maintain the integrity of the connections during and after the soldering process.
Circuit card assembly (CCA) takes PCB assembly a step further. It involves the integration of multiple PCBs and other elements into a single, more complex module. This higher-level assembly is crucial for electronic devices that require multiple interconnected boards to perform their functions.
Component placement is a vital aspect of CCA. It determines the efficiency of the board's operation and its ability to fit within the designated space in the final product. Advanced machines are used to place components with incredible accuracy, ensuring that the assembly is compact and free of errors.
The ultimate goal of CCA is to ensure that the final product performs reliably under all conditions. This means that every aspect of the assembly process, from the soldering techniques to the quality of the electronic components used, must be optimized to produce a durable and effective product.
Electronics manufacturing is an ever-evolving field, with new technologies and processes emerging regularly. Innovations in PCB and CCA are driven by the need for more powerful, efficient, and miniaturized electronic devices. As the industry moves forward, the experience with circuit card assembly will continue to be a blend of precision engineering and cutting-edge technology.
A PCB is a board with electronic components and circuits printed on it, while CCA refers to the assembly of one or more PCBs along with other components into a complete module ready for use in electronic devices.
Quality control ensures that the assembled PCBs meet industry standards for reliability and performance. It involves rigorous testing at various stages to detect and rectify any defects, ensuring high-quality final products.
Wave soldering is a method used to attach electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB. It involves passing the board over a wave of molten solder, creating strong and durable connections.
SMT assembly involves placing smaller components onto the PCB, allowing for more compact and high-density designs. This method uses solder paste and reflow soldering to create connections, making it suitable for modern electronics.
A solder mask prevents short circuits by protecting the copper traces on the PCB from accidental contact with solder or conductive bits. It defines where solder should be applied, ensuring the integrity of the connections.
Reflow soldering involves heating the PCB in a reflow oven after component placement. The heat melts the solder paste, allowing it to flow and create solid connections between the components and the board. Once cooled, the solder solidifies, completing the assembly.
The reliability and performance of a CCA depend on the quality of the electronic components, the precision of the component placement, the effectiveness of the soldering techniques used, and the overall design and assembly process. Ensuring these factors are optimized is crucial for producing durable and high-performing electronic devices.
In conclusion, circuit card assembly is a vital component of the electronics manufacturing process. From the careful placement of integrated circuits to the rigorous quality control measures, every step is designed to ensure the reliability and performance of the final product. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the methods and techniques used in PCB and CCA, driving the industry towards even greater innovations and efficiencies.