In the world of electronics, the term "empty PCB board" might not immediately spark excitement, but these unassuming pieces of material are the backbone of countless devices. From smartphones to microwave ovens, empty PCB boards, also known as printed circuit boards, play a crucial role in the functioning of electronic components. This article delves into the importance of empty PCB boards, their structure, and their applications in modern technology.
What is an Empty PCB Board?
An empty PCB board is essentially a flat sheet, typically made of fiberglass, composite epoxy, or other laminate material, that serves as the foundation for mounting various electronic components. Before any components are added, it is referred to as an "empty" PCB board. Once the components are mounted and the electrical connections are made, it becomes a fully functional printed circuit board.
The primary purpose of an empty PCB board is to provide a platform where electronic components can be interconnected in a reliable and organized manner. These boards are essential for ensuring that electronic devices operate efficiently and effectively.
The Structure of an Empty PCB Board
Empty PCB boards are composed of several layers, each serving a specific function:
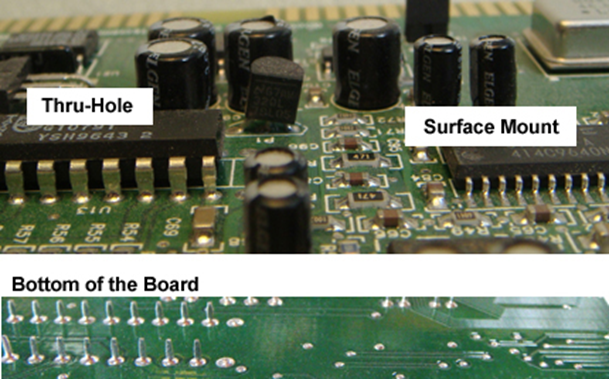
Substrate: This is the base material, typically made of fiberglass or other durable materials, providing mechanical support to the board.
Copper Layer: A thin layer of copper is laminated onto the substrate, forming the conductive pathways for electrical signals.
Solder Mask: This layer is applied over the copper to prevent short circuits and protect the copper traces from environmental damage.
Silkscreen: The top layer, which contains printed information such as component labels and reference designators, aiding in the assembly process.
Each of these layers plays a vital role in the functionality and reliability of the printed circuit board.
Applications of Empty PCB Boards
Empty PCB boards are used in a wide range of applications, from simple electronic gadgets to complex industrial machinery. Here are some common uses:
Consumer Electronics: Devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops rely heavily on printed circuit boards to house and connect their components.
Automotive Industry: Modern vehicles use PCBs for various functions, including engine control units, infotainment systems, and safety features.
Medical Devices: Medical equipment such as MRI machines, pacemakers, and diagnostic tools utilize PCBs for their critical operations.
Industrial Equipment: Machinery used in manufacturing, robotics, and automation systems depend on PCBs for efficient control and operation.
The versatility and reliability of empty PCB boards make them indispensable in virtually every sector that involves electronics.
Advantages of Using Empty PCB Boards
There are several benefits to using empty PCB boards in electronic devices:
Compact Size: PCBs allow for the miniaturization of electronic devices by providing a compact and organized way to connect components.
High Reliability: The structured layout of PCBs reduces the risk of short circuits and improves the overall reliability of the device.
Ease of Maintenance: The standardized design of PCBs makes it easier to troubleshoot and repair electronic devices.
Cost-Effective: Mass production of PCBs reduces manufacturing costs, making electronic devices more affordable.
These advantages underscore the importance of empty PCB boards in the design and manufacturing of modern electronics.
Challenges in PCB Manufacturing
Despite their numerous benefits, the manufacturing of empty PCB boards comes with its own set of challenges:
Design Complexity: As electronic devices become more advanced, the design of PCBs becomes increasingly complex, requiring sophisticated software and expertise.
Material Quality: The quality of the materials used in PCB manufacturing can significantly impact the performance and durability of the final product.
Precision: The manufacturing process must be highly precise to ensure that the copper traces and other elements are accurately placed.
Environmental Concerns: The production of PCBs involves chemicals and processes that can be harmful to the environment if not managed properly.
Overcoming these challenges requires continuous innovation and adherence to strict quality control standards.
Future Trends in PCB Technology
The field of PCB technology is constantly evolving, with several emerging trends that promise to shape the future of electronics:
Flexible PCBs: These boards can bend and flex, making them ideal for wearable technology and other applications where space is limited.
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs: These boards offer higher component density and improved performance, catering to the demands of modern electronics.
Eco-Friendly Materials: There is a growing focus on using environmentally friendly materials and processes in PCB manufacturing to reduce the ecological footprint.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Innovations such as 3D printing and automated assembly are revolutionizing the way PCBs are produced.
These trends highlight the ongoing advancements in PCB technology and their potential to drive future innovations in the electronics industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between an empty PCB board and a printed circuit board?
An empty PCB board is an unpopulated board without any electronic components. Once components are mounted and connected, it becomes a printed circuit board (PCB).
2. Why are empty PCB boards important in electronics?
Empty PCB boards provide a stable and organized platform for mounting and connecting electronic components, ensuring the reliable operation of electronic devices.
3. What materials are used to make empty PCB boards?
Empty PCB boards are typically made of fiberglass, composite epoxy, or other laminate materials, with a copper layer for conductive pathways.
4. How are empty PCB boards manufactured?
The manufacturing process involves layering materials, etching copper traces, applying solder masks, and printing silkscreen information, followed by quality control checks.
5. What are the common applications of empty PCB boards?
Empty PCB boards are used in consumer electronics, automotive systems, medical devices, industrial equipment, and many other applications.